How to Read a Moyno Pump Curve: A Simple Guide
Understanding the performance characteristics of a Moyno pump is crucial for ensuring optimal operation in various applications. A Moyno pump curve provides essential information about how the pump will perform under different conditions. This guide will walk you through the components of a Moyno pump curve and how to interpret it effectively.
What is a Moyno Pump Curve?
A Moyno pump curve is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between the flow rate and the head (pressure) of the pump. It helps users determine the pump’s efficiency, operational limits, and suitability for specific applications. Familiarizing yourself with this curve is essential for selecting the right pump and troubleshooting performance issues.
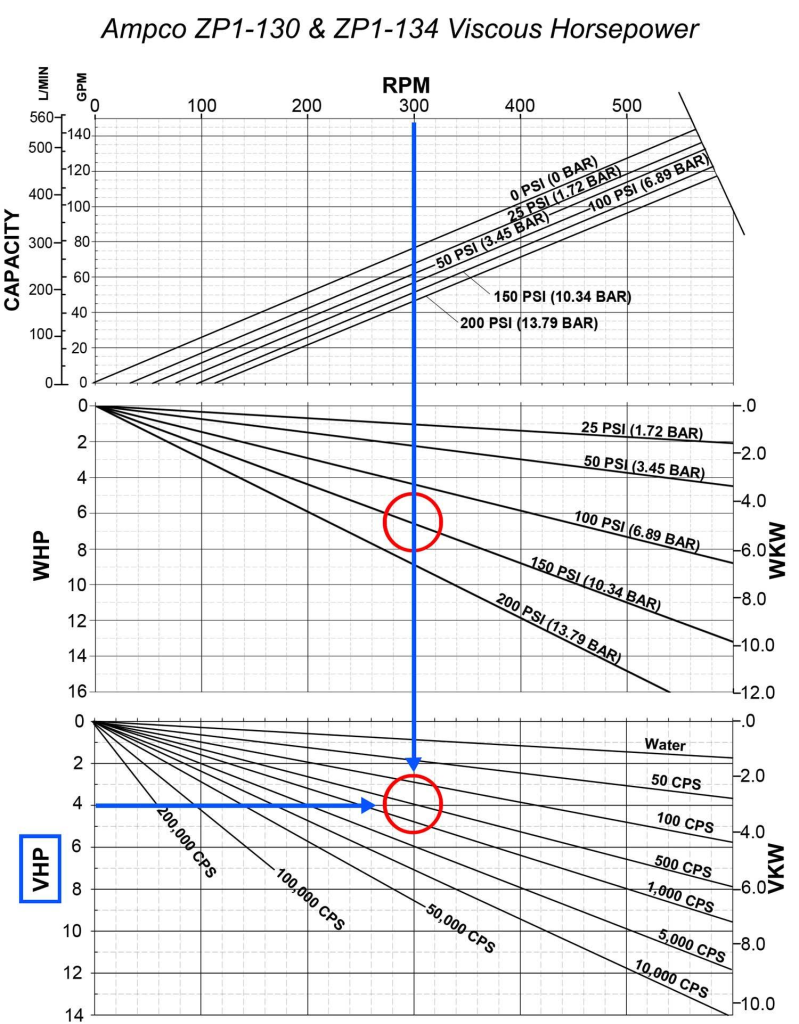
Key Components of the Moyno Pump Curve
To effectively read a Moyno pump curve, it’s important to understand its key components:
- Flow Rate: Typically represented on the horizontal axis, this indicates the volume of fluid the pump can move over time.
- Head: Shown on the vertical axis, this represents the pressure generated by the pump, which is crucial for overcoming system resistance.
- Efficiency: Often illustrated with separate curves, efficiency helps identify how well the pump converts input power into hydraulic energy.
- NPSH Required (Net Positive Suction Head): This curve indicates the minimum pressure required at the pump inlet to avoid cavitation, which can damage the pump.
- Operating Regions: The curve may also display different operating regions, such as the best efficiency point (BEP), which is where the pump operates most effectively.
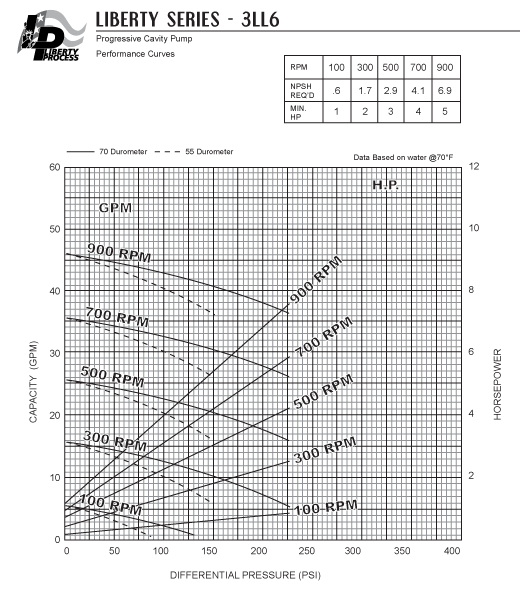
Steps to Read the Moyno Pump Curve
Reading a Moyno pump curve can seem daunting at first, but following these steps can simplify the process:
- Identify Your Requirements: Determine the flow rate and head needed for your application.
- Locate the Operating Point: Find the point on the curve that matches your required flow rate and head. This point will help you assess if the pump is suitable for your needs.
- Check Efficiency: Look for the efficiency curves to ensure that the pump will operate within an acceptable efficiency range. Higher efficiency translates to lower operating costs.
- Evaluate NPSH: Ensure that the NPSH available in your system exceeds the NPSH required by the pump to avoid cavitation.
- Consider Operating Limits: Review the curve for any limitations that may affect performance, such as maximum flow rates or pressures.
Conclusion
Reading a Moyno pump curve is an essential skill for anyone involved in pump selection and operation. By understanding the key components and following a systematic approach, you can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and reliability of your pumping system. Whether you are designing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one, mastering the Moyno pump curve will empower you to achieve optimal performance.
